Abstract
Summary
The ROSE study compared annual infusion with zoledronic acid and weekly generic alendronate. No significant differences in quality of life or health status between treatment groups were observed. Adherence to alendronate during the study was high, with 80.9% of patients achieving adequate adherence.
Introduction
A secondary analysis to evaluate quality of life, health status, adherence to alendronate and therapy preference in postmenopausal women with low bone mass who received treatment with zoledronic acid or alendronate was conducted.
Methods
Postmenopausal women with low bone mass were randomised 2:1 to receive an annual infusion of zoledronic acid or weekly oral generic alendronate in this open-label, multicentre study. Changes in quality of life and health status were assessed using questionnaires at baseline and month 12. Adherence to alendronate was assessed by the investigator and/or study personnel, and subjective therapy preference was assessed using a questionnaire at month 12.
Results
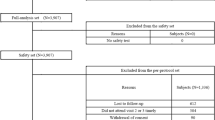
Patients were randomised to zoledronic acid (n = 408) and alendronate (n = 191). Overall, there were no significant differences in quality of life between zoledronic acid and alendronate. However, improvements in quality of life with zoledronic acid versus alendronate could be detected by posthoc analysis in patients with previous fractures. There were no significant differences in health status between patients receiving zoledronic acid or alendronate. Adherence to alendronate during the study was high, with 80.9% of patients achieving adequate adherence. A total of 81% of patients who had received zoledronic acid indicated that they would prefer to continue with that treatment, and 43% of the patients who received oral alendronate would like to switch to zoledronic acid.
Conclusions
There were no significant differences in quality of life between patients receiving zoledronic acid or alendronate.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bock O, Felsenberg D (2008) Bisphosphonates in the management of postmenopausal osteoporosis—optimizing efficacy in clinical practice. Clin Interv Aging 3:279–297
Abrahamsen B, van Staa T, Ariely R et al (2009) Excess mortality following hip fracture: a systematic epidemiological review. Osteoporos Int 20:1633–1650
Cosman F (2009) Treatment of osteoporosis and prevention of new fractures: role of intravenously administered bisphosphonates. Endocr Pract 15:483–493
Cramer JA, Gold DY, Silverman SL et al (2007) A systematic review of persistence and compliance with bisphosphonates for osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 18:1023–1031
Ziller V, Wetzel K, Kyvernitakis I et al (2011) Adherence and persistence in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis treated with raloxifene. Climacteric 14(2):228–235
Ziller V, Zimmerman SP, Kalder M et al (2010) Adherence and persistence in patients with severe osteoporosis treated with teriparatide. Curr Med Res Opin 26:675–681
Hadji P, Claus V, Ziller V et al (2011) GRAND: the German retrospective cohort analysis on compliance and persistence and the associated risk of fractures in osteoporotic women treated with oral bisphosphonates. Osteoporos Int. doi:10.1007/s00198-011-1535-z
Landfeldt E, Ström O, Robbins S et al (2011) Adherence to treatment of primary osteoporosis and its association to fractures—the Swedish Adherence Register Analysis (SARA). Osteoporos Int. doi:10.1007/s00198-011-1549-6
Siris ES, Harris ST, Rosen CJ et al (2006) Adherence to bisphosphonate therapy and fracture rates in osteoporotic women: relationship to vertebral and nonvertebral fractures from 2 US claims databases. Mayo Clin Proc 81:1013–1022
Imaz I, Zegarra P, Gonzalez-Enriquez J et al (2010) Poor bisphosphonate adherence for treatment of osteoporosis increases fracture risk: systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 21(11):1943–1951
Höer A, Seidlitz C, Gothe H et al (2009) Influence on persistence and adherence with oral bisphosphonates on fracture rates in osteoporosis. Patient Pref Adherence 3:25–30
Blouin J, Dragomir A, Moride Y et al (2009) Impact of non-compliance with alendronate and risedronate. Br J Clin Pharmacol 66:117–127
Cockerill W, Lunt M, Silman AJ et al (2004) Health-related quality of life and radiographic vertebral fracture. Osteoporos Int 15:113–119
Cooper C, Jakob F, Chinn C et al (2008) Fracture incidence and changes in quality of life in women with an inadequate clinical outcome from osteoporosis therapy: the Observational Study of Severe Osteoporosis (OSSO). Osteoporos Int 19:493–501
Boonen S, Vanderschueren D, Venken K et al (2008) Recent developments in the management of postmenopausal osteoporosis with bisphosphonates: enhanced efficacy by enhanced compliance. J Intern Med 264:315–332
Cooper A, Drake J, Brankin E, Investigators PERSIST (2006) Treatment persistence with once-monthly ibandronate and patient support vs. once-weekly alendronate: results from the PERSIST study. Int J Clin Pract 60:896–905
Hadji P, Minne H, Pfeifer M et al (2008) Treatment preference for monthly oral ibandronate and weekly oral alendronate in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized, crossover study (BALTO II). Joint Bone Spine 75:303–310
Black DM, Delmas PD, Eastell R et al (2007) Once-yearly zoledronic acid for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. N Engl J Med 356:1809–1822
Lyles KW, Colón-Emeric CS, Magaziner JS (2007) Zoledronic acid in reducing clinical fracture and mortality after hip fracture. N Engl J Med 357:1799–1809
Hadji P, Gamerdinger D, Spieler W et al (2011) Rapid Onset and Sustained Efficacy (ROSE) study: results of a randomised, multicentre trial comparing the effect of zoledronic acid or alendronate on bone metabolism in postmenopausal women with low bone mass. Osteoporos Int. doi:10.1007/s00198-011-1583-4
de Oliveira FN, Arthuso M, da Silva R et al (2009) Quality of life in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: correlation between QUALEFFO 41 and SF-36. Maturitas 62:85–90
Lips P, Jameson K, Bianchi ML, Working Group for Quality of Life of the International Osteoporosis Foundation et al (2010) Validation of the IOF quality of life questionnaire for patients with wrist fracture. Osteoporos Int 21(1):61–70
Nevitt MC, Thompson DE, Black DM et al (2000) Effect of alendronate on limited-activity days and bed-disability days caused by back pain in postmenopausal women with existing vertebral fractures. Arch Intern Med 160:77–85
Cauley JA, Black D, Boonen S, et al (2010) Once-yearly zoledronic acid and days of disability, bed rest and back pain: randomised controlled HORIZON pivotal fracture trial. J Bone Miner Res epub ahead of print
Ettinger B, Black DM, Mitlak BH et al (1999) Reduction of vertebral fracture risk in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis treated with raloxifene: results from a randomized clinical trial. Multiple outcomes of Raloxifene Evaluation (MORE) Investigators. JAMA 282:637–645
Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB et al (1996) Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Fracture Intervention Trial Research Group. Lancet 348:1535–1541
Kendler DL, McClung MR, Freemantle N et al (2011) Adherence, preference, and satisfaction of postmenopausal women taking denosumab or alendronate. Osteoporos Int 22(6):1725–1735
Bartl R, Gotte S, Hadji P et al (2006) [Adherence with daily and weekly administration of oral bisphosphonates for osteoporosis treatment]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 131:1257–1262
Copher R, Buzinec P, Zarotsky V et al (2010) Physician perception of patient adherence compared to patient adherence of osteoporosis medications from pharmacy claims. Curr Med Res Opin 26:777–785
Ettinger MP, Gallagher R, MacCosbe PE (2006) Medication persistence with weekly versus daily doses of orally administered bisphosphonates. Endocr Pract 12:522–528
Cotté FE, Fardellone P, Mercier F et al (2010) Adherence to monthly and weekly oral bisphosphonates in women with osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 21:145–155
Wilkes MM, Navickis RJ, Chan WW et al (2010) Bisphosphonates and osteoporotic fractures: a cross-design synthesis of results among compliant/persistent postmenopausal women in clinical practice versus randomized controlled trials. Osteoporos Int 21:679–688
Emkey R, Koltun W, Beusterien K et al (2005) Patient preference for once-monthly ibandronate in a randomized, open-label, cross-over trial: the Bonviva Alendronate Trial in Osteoporosis (BALTO). Curr Med Res Opin 21:1895–1903
Hadji P, Benhamou CL, Devas V et al (2008) Treatment preference for monthly oral ibandronate and weekly oral alendronate in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a randomized, crossover study (BALTO II). Joint Bone Spine 75(3):303–310
McClung M, Recker R, Miller P et al (2007) Intravenous zoledronic acid 5 mg in the treatment of postmenopausal women with low bone density previously treated with alendronate. Bone 41:122–128
Saag K, Lindsay R, Kriegman A et al (2007) A single zoledronic acid infusion reduces bone resorption markers more rapidly than weekly oral alendronate in postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. Bone 40:1238–1243
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to all the administrators of each of the 95 sites that participated in this study for their contribution and support. Medical writing support was provided by Caroline Masterman, ACUMED® (Tytherington, UK), with funding from Novartis Pharma GmbH, Nuremberg, Germany.
Conflicts of interest
Dr. P. Hadji has received honoraria, unrestricted educational grants and research funding from the following companies: Amgen, AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche and Wyeth. Dr. P. H. Kann, Dr. V. Ziller, Dr. W. Spieler, Mr. Gamerdinger and Dr. Moricke have no conflicts of interest. Dr. M Baier and Dr. K. Articus are employees of Novartis Pharma GmbH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hadji, P., Ziller, V., Gamerdinger, D. et al. Quality of life and health status with zoledronic acid and generic alendronate—a secondary analysis of the Rapid Onset and Sustained Efficacy (ROSE) study in postmenopausal women with low bone mass. Osteoporos Int 23, 2043–2051 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-011-1834-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-011-1834-4