Abstract
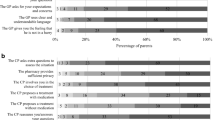
Background Epilepsy is a chronic condition requiring compliance to long treatment regimes. Knowledge on epilepsy can affect compliance to treatment. Pediatric epileptic patients need caregivers for their care; however, prior research showed that caregivers had inadequate knowledge in epilepsy. In view of this, outpatient pharmacist epilepsy service was set up in collaboration with neurologists to bridge knowledge gaps. Objective To determine if caregiver education provided by outpatient pharmacists is associated with improved knowledge in epilepsy and its management. Setting Pediatric outpatient clinic at a pediatric and women’s health hospital. Methods A cross-sectional pre- to post-intervention study using scores of caregiver knowledge of epilepsy as the primary outcome was conducted. The intervention was one counseling session by pharmacists. A knowledge questionnaire (A) was administered to the caregiver to obtain baseline information before the session and readministered by telephone (C) 2 weeks post-session. Additionally, a perception questionnaire (B) was administered immediately after the session. Main outcome measure Knowledge scores pre and post pharmacist counseling. Results Twenty-seven completed questionnaire sets (A, B and C) were collected from 55 caregivers who received the intervention (response rate = 49 %) between September 2010 and May 2011. Average post-counseling knowledge scores was significantly higher than pre-counseling scores (14.7 vs. 10.4, p = 0.000) (score range −21 to 21). Caregivers’ confidence to administer antiepileptic drugs to the child increased significantly from 3.60 to 3.94 post-counseling (p = 0.002, score range 0–5). Mean total satisfaction score was 36.00 (score range 5–40). Conclusion A specialized counseling session given by pharmacists increased caregiver’s knowledge about epilepsy and medication adherence. The session was well received by caregivers. Pharmacists should continue to be involved in the care of epileptic patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
McAuley JW, Miller MA, Klatte E, Shneker BF. Patients with epilepsy’s perception on community pharmacist’s current and potential role in their care. Epilepsy Behav. 2009;14:141–5.
Lewis C, Scott D, Pantell R, Wolf M. Parent satisfaction with children’s medical care: development, field test, and validation of a questionnaire. Med Care. 1986;24(3):209–15.
Garnett W. Antiepileptic drug treatment: outcomes and adherence. Pharmacotherapy. 2000;20(8):1991S–9S.
Sabaté E. Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2003:87–93. Chapter 11, Epilepsy; [cited 2013 Feb 19]; Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/42682/1/9241545992.pdf.
Beech L. Knowledge of epilepsy among relatives of the epilepsy sufferer. Seizure. 1992;1:133–5.
Singhal PK, Raisch DW, Gupchup GV. The impact of pharmaceutical services in community and ambulatory care settings: evidence and recommendations for future research. Ann Pharmacother. 1993;33:1336–55.
Murray M. Continuity of health care and the pharmacists: let’s keep it simple. Ann Pharmacother. 2009;43:745–7.
Ellitt GR, Brien JAE, Aslani P, Chen TF. Quality patient care and pharmacists’ role in it’s continuity-a systematic review. Ann Pharmacother. 2009;43:677–90.
Elliott J, Shneker B. Patient, caregiver, and healthcare practitioner knowledge of, beliefs about, and attitudes toward epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2008;12:547–56.
Chan D, Phuah H, Ng Y, Choong C, Lim K, Goh W. Pediatric epilepsy and first afebrile seizure in Singapore: epidemiology and investigation yield at presentation. J Child Neurol. 2010;25(10):1–7.
Liu L, Yiu C, Yen D, Chou M, Lin M. Medication education for patients with epilepsy in Taiwan. Seizure. 2003;12:473–8.
Larson L, Rovers J, MacKeigan L. Patient satisfaction with pharmaceutical care: update of a validated instrument. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2002;42(1):44–9.
Galleti F, Sturniolo MG. Counseling children and parents about epilepsy. Patient Educ Couns. 2004;55:422–5.
Saengsuwan J, Laohasiriwong W, Boonyaleepan S, Sawanyawisuth K, Tiamkao S. Integrated epilepsy research group. Knowledge, attitudes, and care techniques of caregivers of PWE in northeastern Thailand. Epilepsy Behav. 2013;27:257–63.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the doctors and nurses of the KKH Pediatric Medicine Neurology team, and the Department of Pharmacy, without which this project would not have been possible. Also we would like to thank Dr Desiree Lie, Dr Derrick Chan and Dr Joseph Bertino for kindly reviewing the manuscript.
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Lee, D.S.H. & Hie, S.L. The impact of pharmacist’s counseling on pediatric patients’ caregiver’s knowledge on epilepsy and its treatment in a tertiary hospital. Int J Clin Pharm 35, 829–834 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-013-9817-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-013-9817-5